Functions which set the hyperparameters, seeds, and prior
weight for each model to be used in Bayesian model averaging
via dreamer_mcmc().
See each function's section below for the model's details. In the following, \(y\) denotes the response variable and \(d\) represents the dose.
For the longitudinal specifications, see documentation on
model_longitudinal.
model_linear(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_quad(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_loglinear(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_logquad(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_emax(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
mu_b4,
sigma_b4,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_exp(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
shape,
rate,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_beta(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
mu_b4,
sigma_b4,
shape,
rate,
scale = NULL,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_independent(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
shape,
rate,
doses = NULL,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_linear_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_quad_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_loglinear_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_logquad_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_emax_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
mu_b4,
sigma_b4,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_exp_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_beta_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
mu_b2,
sigma_b2,
mu_b3,
sigma_b3,
mu_b4,
sigma_b4,
scale = NULL,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)
model_independent_binary(
mu_b1,
sigma_b1,
doses = NULL,
link,
w_prior = 1,
longitudinal = NULL
)Arguments
- mu_b1, sigma_b1, mu_b2, sigma_b2, mu_b3, sigma_b3, mu_b4, sigma_b4, shape, rate
models parameters. See sections below for interpretation in specific models.
- w_prior
a scalar between 0 and 1 indicating the prior weight of the model.
- longitudinal
output from a call to one of the model_longitudinal_*() functions. This is used to specify a longitudinal dose-response model.
- scale
a scale parameter in the Beta model. Default is 1.2 * max(dose).
- doses
the doses in the dataset to be modeled. The order of the doses corresponds to the order in which the priors are specified in
mu_b1andsigma_b1.- link
a character string of either "logit" or "probit" indicating the link function for binary model.
Value
A named list of the arguments in the function call. The list has
S3 classes assigned which are used internally within dreamer_mcmc().
Linear
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * d$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
Quadratic
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * d + b_3 * d^2$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
Log-linear
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * log(d + 1)$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
Log-quadratic
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * log(d + 1) + b_3 * log(d + 1)^2$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
EMAX
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + (b_2 - b_1) * d ^ b_4 / (exp(b_3 * b_4) + d ^ b_4)$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$ $$b_4 \sim N(mu_b4, sigma_b4 ^ 2), (Truncated above 0)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$ Here, \(b_1\) is the placebo effect (dose = 0), \(b_2\) is the maximum treatment effect, \(b_3\) is the \(log(ED50)\), and \(b_4\) is the hill or rate parameter.
Exponential
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * (1 - exp(- b_3 * d))$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2), (truncated to be positive)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
Beta
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_1 + b_2 * ((b3 + b4) ^ (b3 + b4)) / (b3 ^ b3 * b4 ^ b4) * (d / scale) ^ b3 * (1 - d / scale) ^ b4$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2), Truncated above 0$$ $$b_4 \sim N(mu_b4, sigma_b4 ^ 2), Truncated above 0$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$ Note that \(scale\) is a hyperparameter specified by the user.
Independent
$$y \sim N(f(d), \sigma^2)$$ $$f(d) = b_{1d}$$ $$b_{1d} \sim N(mu_b1[d], sigma_b1[d] ^ 2)$$ $$1 / \sigma^2 \sim Gamma(shape, rate)$$
Independent Details
The independent model models the effect of each dose independently.
Vectors can be supplied to mu_b1 and sigma_b1 to set a different
prior for each dose in the order the doses are supplied to doses.
If scalars are supplied to mu_b1 and sigma_b1, then the same prior
is used for each dose, and the doses argument is not needed.
Linear Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * d$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$
Quadratic Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * d + b_3 * d^2$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$
Log-linear Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * log(d + 1)$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$
Log-quadratic Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * log(d + 1) + b_3 * log(d + 1)^2$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$
EMAX Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + (b_2 - b_1) * d ^ b_4 / (exp(b_3 * b_4) + d ^ b_4)$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2)$$ $$b_4 \sim N(mu_b4, sigma_b4 ^ 2), (Truncated above 0)$$ Here, on the \(link(f(d))\) scale, \(b_1\) is the placebo effect (dose = 0), \(b_2\) is the maximum treatment effect, \(b_3\) is the \(log(ED50)\), and \(b_4\) is the hill or rate parameter.
Exponential Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * (exp(b_3 * d) - 1)$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2), (Truncated below 0)$$
Beta Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d)$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_1 + b_2 * ((b3 + b4) ^ (b3 + b4)) / (b3 ^ b3 * b4 ^ b4) * (d / scale) ^ b3 * (1 - d / scale) ^ b4$$ $$b_1 \sim N(mu_b1, sigma_b1 ^ 2)$$ $$b_2 \sim N(mu_b2, sigma_b2 ^ 2)$$ $$b_3 \sim N(mu_b3, sigma_b3 ^ 2), Truncated above 0$$ $$b_4 \sim N(mu_b4, sigma_b4 ^ 2), Truncated above 0$$ Note that \(scale\) is a hyperparameter specified by the user.
Independent Binary
$$y \sim Binomial(n, f(d))$$ $$link(f(d)) = b_{1d}$$ $$b_{1d} \sim N(mu_b1[d], sigma_b1[d]) ^ 2$$
Independent Binary Details
The independent model models the effect of each dose independently.
Vectors can be supplied to mu_b1 and sigma_b1 to set a different
prior for each dose in the order the doses are supplied to doses.
If scalars are supplied to mu_b1 and sigma_b1, then the same prior
is used for each dose, and the doses argument is not needed.
Longitudinal Linear
Let \(f(d)\) be a dose response model. The expected value of the response, y, is: $$E(y) = g(d, t)$$ $$g(d, t) = a + (t / t_max) * f(d)$$ $$a \sim N(mu_a, sigma_a)$$
Longitudinal ITP
Let \(f(d)\) be a dose response model. The expected value of the response, y, is: $$E(y) = g(d, t)$$ $$g(d, t) = a + f(d) * ((1 - exp(- c1 * t))/(1 - exp(- c1 * t_max)))$$ $$a \sim N(mu_a, sigma_a)$$ $$c1 \sim Uniform(a_c1, b_c1)$$
Longitudinal IDP
Increasing-Decreasing-Plateau (IDP).
Let \(f(d)\) be a dose response model. The expected value of the response, y, is: $$E(y) = g(d, t)$$ $$g(d, t) = a + f(d) * (((1 - exp(- c1 * t))/(1 - exp(- c1 * d1))) * I(t < d1) + (1 - gam * ((1 - exp(- c2 * (t - d1))) / (1 - exp(- c2 * (d2 - d1))))) * I(d1 <= t <= d2) + (1 - gam) * I(t > d2))$$ $$a \sim N(mu_a, sigma_a)$$ $$c1 \sim Uniform(a_c1, b_c1)$$ $$c2 \sim Uniform(a_c2, b_c2)$$ $$d1 \sim Uniform(0, t_max)$$ $$d2 \sim Uniform(d1, t_max)$$ $$gam \sim Uniform(0, 1)$$
Examples
set.seed(888)
data <- dreamer_data_linear(
n_cohorts = c(20, 20, 20),
dose = c(0, 3, 10),
b1 = 1,
b2 = 3,
sigma = 5
)
# Bayesian model averaging
output <- dreamer_mcmc(
data = data,
n_adapt = 1e3,
n_burn = 1e2,
n_iter = 1e3,
n_chains = 2,
silent = TRUE,
mod_linear = model_linear(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2
),
mod_quad = model_quad(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
mu_b3 = 0,
sigma_b3 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2
)
)
# posterior weights
output$w_post
#> mod_linear mod_quad
#> 0.7036919 0.2963081
# plot posterior dose response
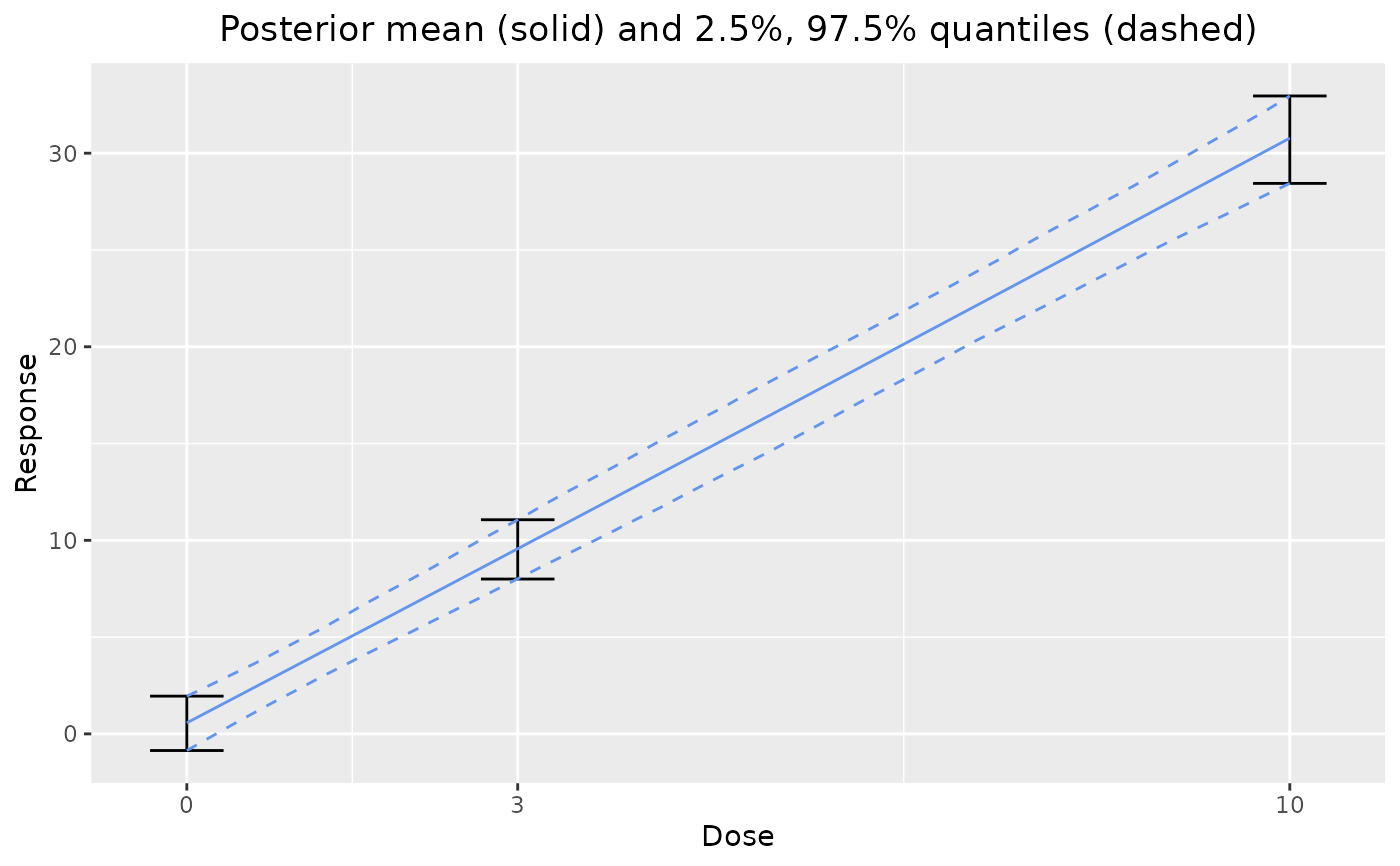
plot(output)
 # LONGITUDINAL
library(ggplot2)
set.seed(889)
data_long <- dreamer_data_linear(
n_cohorts = c(10, 10, 10, 10), # number of subjects in each cohort
doses = c(.25, .5, .75, 1.5), # dose administered to each cohort
b1 = 0, # intercept
b2 = 2, # slope
sigma = .5, # standard deviation,
longitudinal = "itp",
times = c(0, 12, 24, 52),
t_max = 52, # maximum time
a = .5,
c1 = .1
)
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
ggplot(data_long, aes(time, response, group = dose, color = factor(dose))) +
geom_point()
} # }
output_long <- dreamer_mcmc(
data = data_long,
n_adapt = 1e3,
n_burn = 1e2,
n_iter = 1e3,
n_chains = 2,
silent = TRUE, # make rjags be quiet,
mod_linear = model_linear(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2, # prior probability of the model
longitudinal = model_longitudinal_itp(
mu_a = 0,
sigma_a = 1,
a_c1 = 0,
b_c1 = 1,
t_max = 52
)
),
mod_quad = model_quad(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
mu_b3 = 0,
sigma_b3 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2,
longitudinal = model_longitudinal_linear(
mu_a = 0,
sigma_a = 1,
t_max = 52
)
)
)
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# plot longitudinal dose-response profile
plot(output_long, data = data_long)
plot(output_long$mod_quad, data = data_long) # single model
# plot dose response at final timepoint
plot(output_long, data = data_long, times = 52)
plot(output_long$mod_quad, data = data_long, times = 52) # single model
} # }
# LONGITUDINAL
library(ggplot2)
set.seed(889)
data_long <- dreamer_data_linear(
n_cohorts = c(10, 10, 10, 10), # number of subjects in each cohort
doses = c(.25, .5, .75, 1.5), # dose administered to each cohort
b1 = 0, # intercept
b2 = 2, # slope
sigma = .5, # standard deviation,
longitudinal = "itp",
times = c(0, 12, 24, 52),
t_max = 52, # maximum time
a = .5,
c1 = .1
)
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
ggplot(data_long, aes(time, response, group = dose, color = factor(dose))) +
geom_point()
} # }
output_long <- dreamer_mcmc(
data = data_long,
n_adapt = 1e3,
n_burn = 1e2,
n_iter = 1e3,
n_chains = 2,
silent = TRUE, # make rjags be quiet,
mod_linear = model_linear(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2, # prior probability of the model
longitudinal = model_longitudinal_itp(
mu_a = 0,
sigma_a = 1,
a_c1 = 0,
b_c1 = 1,
t_max = 52
)
),
mod_quad = model_quad(
mu_b1 = 0,
sigma_b1 = 1,
mu_b2 = 0,
sigma_b2 = 1,
mu_b3 = 0,
sigma_b3 = 1,
shape = 1,
rate = .001,
w_prior = 1 / 2,
longitudinal = model_longitudinal_linear(
mu_a = 0,
sigma_a = 1,
t_max = 52
)
)
)
if (FALSE) { # \dontrun{
# plot longitudinal dose-response profile
plot(output_long, data = data_long)
plot(output_long$mod_quad, data = data_long) # single model
# plot dose response at final timepoint
plot(output_long, data = data_long, times = 52)
plot(output_long$mod_quad, data = data_long, times = 52) # single model
} # }